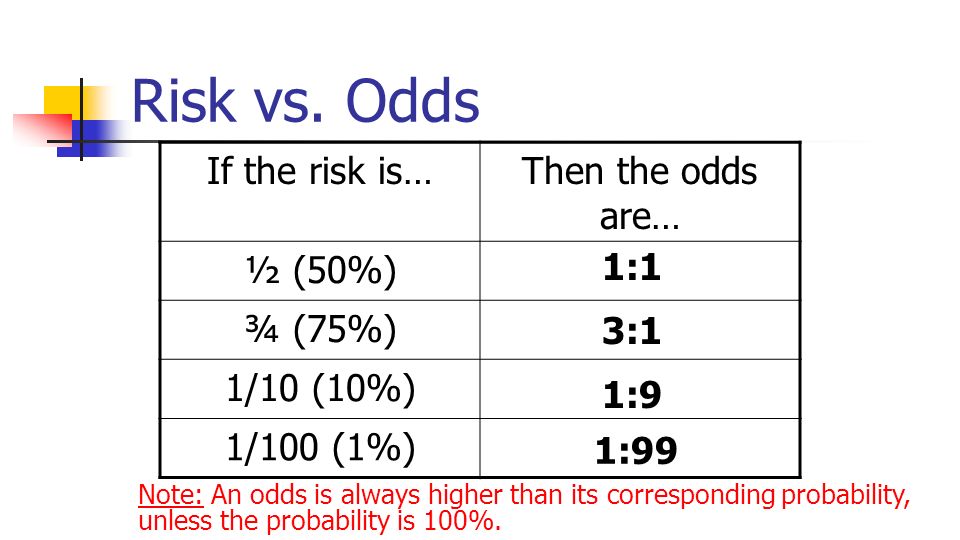
· Risk and Odds Risk vs odds The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different CER = 02 EER = 01 RR = 01 / 02 ARR = 02 – 01 ARR = 01 RRR = 01 / 02 RRR = 05 NNT = 1 / 01 Dr Marc Barton qualified from Imperial College SchoolCommon pitfalls in statistical analysis Odds versus risk In biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variablesIn statistics, however, risk and odds have particular meanings and are calculated in different ways When the difference between them is ignored, the results of a systematic review may be misinterpreted Risk is the concept more familiar to patients and health professionals Risk describes the probability with which a health outcome (usually an adverse event) will occur

Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
Odds ratio vs risk ratio
Odds ratio vs risk ratio-In many clinical papers, probabilities are reported both as 'risk ratios' and 'odds ratios' to indicate similar things However, they are not calculated similarly In this blog, I'll review the basic concepts behind these and examine how they differ with an example · You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with nonsmokers)



Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney
· The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal · Odds ratio is a measure of strength of association between risk factor and outcome/disease in a case control study It is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event occurring in one group to the odds of it occurring in another groupRisks and Odds When talking about the chance of something happening, eg death, hip fracture, we can talk about • risk and relative risk or • odds and odds ratio Risks and odds Risks and odds Risks A proportion Numerator / Denominator Odds A ratio Numerator / (Denominator
The relationship between risk and odds is interesting due to the difference in their upper bounds As shown in Table 1, the two are very similar for values near 0 (the lower bound common to each) but diverge quickly as we move away from 0 and approach a risk of 1 (risk's upper limit) This divergence and the odds' infinite upperThe more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 · The fundamental problem is that quoting the odds in group A, divided by the odds in group B, confuses most people because we just don't think in terms of odds The homemade video abstract on the BMJ website shows you the difference between odds and risk, and how one odds ratio can mean several different relative risks (RRs), depending on the
Odds Ratio, Relative Risk, Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial #30 MarinStatsLecturesAmerican Odds are the default odds at American sportsbooks These odds are based on winning $100 for a given bet Betting a Favorite The odds for favorites will have a minus () sign, and represent the money you need to risk to win $100 So if you're betting on the Packers at 140 against the Vikings, that means Green Bay is a slight favoritePortantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998) And it is this fact that enables us, most of the time, to approximate the relative risk with the odds ratio Table 5 below illustrates the relationship between RR and OR for some probabilities of the outcome 3 Relation between RR and HR



Attributable Risk And Odds Ratio Online Medical Library


Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be
/11/18 · To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrence · If we multiply any unexposed outcome odds by an exposure odds ratio greater than 1 and convert the resulting odds when exposed to a risk, that risk will fall between 0 and 1 8,11 Thus, it is always hypothetically possible for an odds ratio to be constant for all individuals in a population 1214 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the odds of another EssoeOdds1


Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
The odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome OR9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effectsEnglish Plot showing the relationship between risk ratio and odds ratio for various baseline risks with y=x in blue for comparison Date 21 February 21 Source Own work Author D Wells SVG development The source code of this SVG is This plot was created with R Rsplus



Comparison Of Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Based On Download Table



Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download
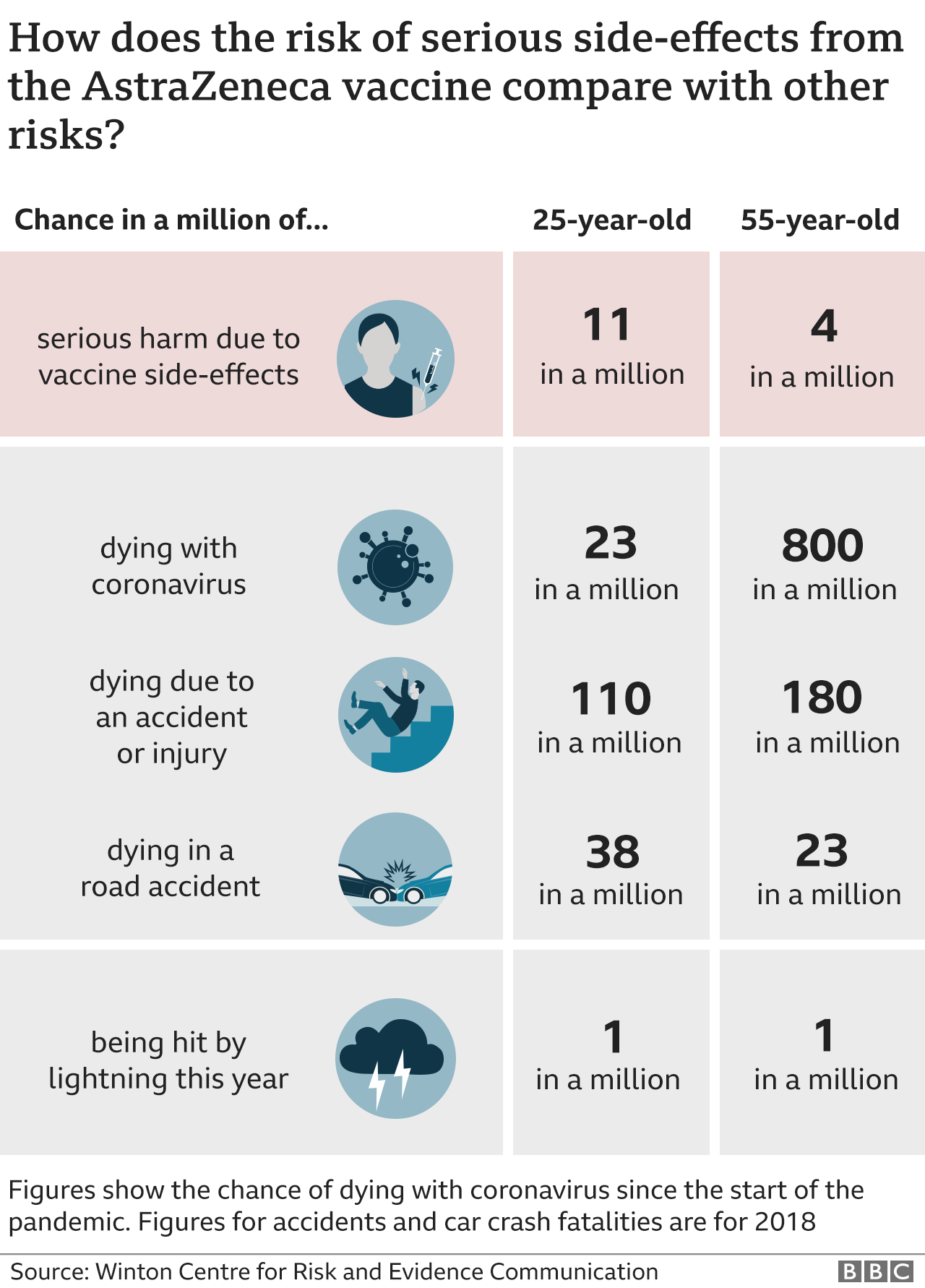
The odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studiesIt can be difficult to accurately assess the biggest risks we face Plane crashes, being struck by lightning, or being attacked by a dog are common fears, but what about falls, the danger inside a bottle of pills, or your drive to work? · Odds ratio (OR), risk ratio (RR), and prevalence ratio (PR) are some of the measures of association which are often reported in research studies quantifying the relationship between an independent variable and the outcome of interest There has been much debate on the issue of which measure is appropriate to report depending on the study design



Odds Ratios Of Risk Factors For The Severity Of Cad By Ethnicity Odds Download Scientific Diagram


Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators · The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the · The risk of failure with SF was 96/351 (27%) vs 32/350 (9%) with HP The RR was 3 This has a very intuitive meaning risk of failure with SF was three times more likely than HP Odds Ratio The OR is a way to present the strength of association between risk



The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chisquare



Evidencebased Journal Club Intentiontotreat Odds And Risk Paul
· The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio)Die OddsRatio (Quotenverhältnis oder Chancenverhältnis) wäre dann 0,28 / 0,16 = 1,75 Ein Wert größer 1 heißt, dass die Quote in der ersten Gruppe größer ist, ein Wert kleiner 1, dass die Odds der ersten Gruppe kleiner sind Ein Wert von 1 ist ein gleiches Quotenverhältnis Nun alles klar mit Risk, Odds und Ratio?Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greater



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
· Explanation and demonstration with simulated data of the difference between relative risk ratios and odds ratios, and how to extract them from a generalized linear model 17 Aug 18 This post tries to explain the difference between odds ratios and relative risk ratios; · Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents · Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (



Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club
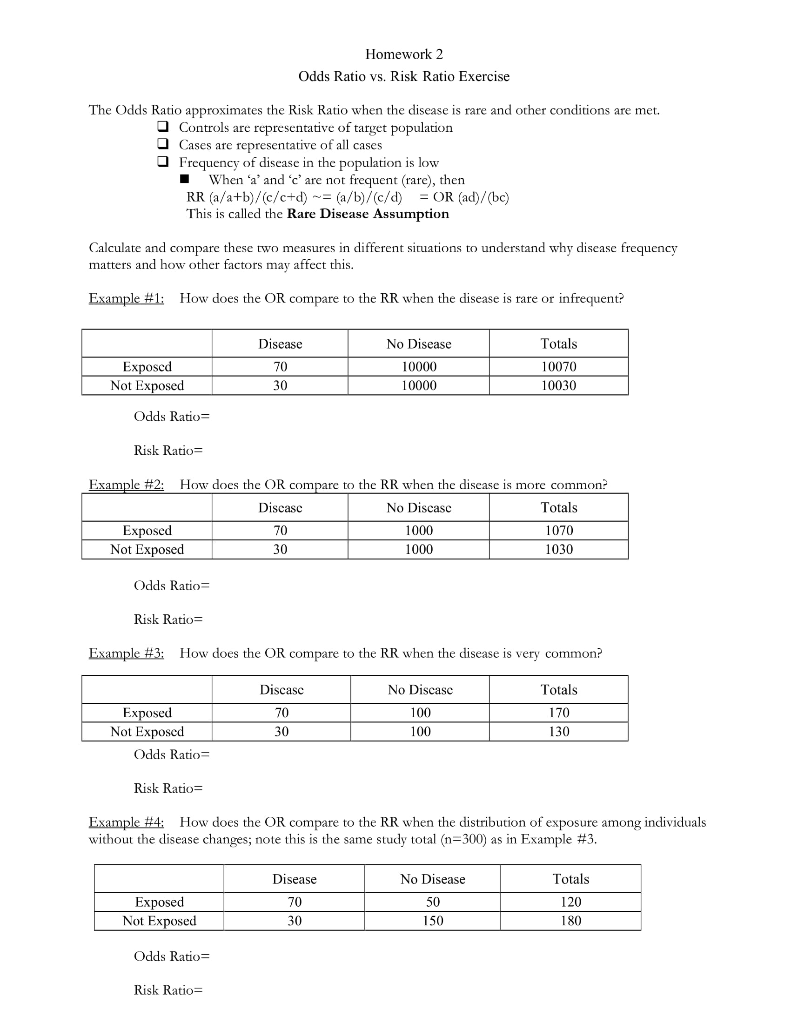


Solved Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Chegg Com
· Even better, you can bet the game in riskfree fashion Bet the Grizzlies riskfree up to $500!Knowing the odds is the first step in beating them But, not all risks faced in life can be accurately estimatedOdds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiert Genau so kommen Experten auf populäre Zeilen wie "Gewöhnliche alkoholische Getränketrinker sind



Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney


Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download
But then the ratio of the risks, which is RR, is approximately equal to the ratio of the odds, which is ORWho's it for New users in TN;In other words, for the exposed population, the risk of developing the disease is approximately equal to the odds Analogous reasoning shows that the risk is approximately equal to the odds for the nonexposed population as well;



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough
· Odds Ratio (OR) is a measure associations between exposure (risk factors) and the incidence of disease;And how just a few letters in the code fitting a generalized linear model · Comparing AstraZeneca vaccine bloodclot risk to odds of dying in a car crash unhelpful, experts say Downplaying the risk with inappropriate comparisons will not build coronavirus vaccine



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Solved Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com
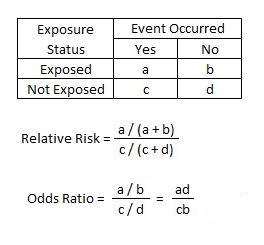
Calculated from the incidence of the disease in at risk groups (exposed to risk factors) compared to the incidence of the disease in nonrisk group (not exposed to a risk factor) · The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/(c/d) = (ad)/(bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/(ab))/(c/(cd)) = (a(cd))/(c(ab)) · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction



Epidemiology Midterm Flashcards Quizlet



Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications
In the "risk" of response and a 60% increase in the "risk" of remission Risk, therefore, is used to reflect probability, regardless of the desirability or undesirability of an event 2 Relative risk is an important and commonly used Odds Ratio · The primary difference between odds and probability is that while odds is a ratio of occurrence to nonoccurrence, the probability is the ratio of occurrence to the whole Odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or in decimal · Risk Odds When Rolling 3 Dice against 2 When rolling 3 attacking dice against 2 defending dice attacker wins 2 3717% attacker wins 1,
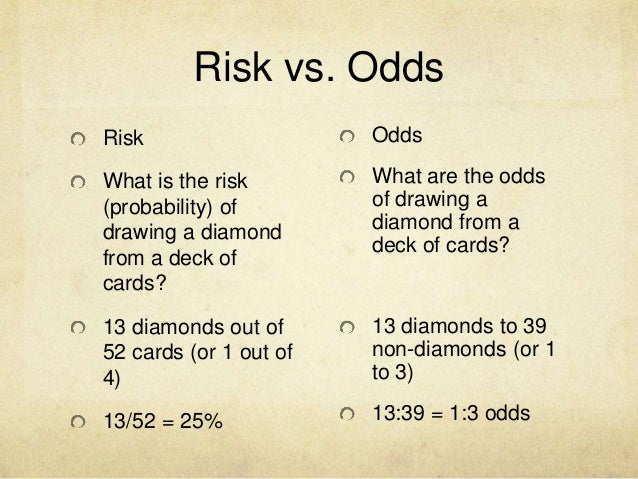


Clinical Epidemiology Bootcamp



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
Here are the details WynnBet Sportsbook Offer Bet the Grizzlies riskfree up to $500 Bet now Click here;The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,New users' first bet will be riskfree up to $500 at WynnBet, and you can use it any way you please



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk


Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated


Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey


Literature Search



Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology


Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology


File Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Svg Wikimedia Commons


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Quantifying Risk Incidence Vs Precision Precision Vs Accuracy Flashcards Quizlet



Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout



Abbreviations Ci Confidence Interval Or Odds Ratio Low Risk Vs Download Scientific Diagram



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio



Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh



Odds Ratio Article



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



The Odds Of Dying Perceived Risk Vs Reality Insure Info Blog



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora


Measures Of Association Ppt Download


Relative Risk Wikipedia



Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Math3010 Week 6



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table


Relative Risk Article


Astrazeneca Vaccine How Do You Weigh Up The Risks And Benefits c News



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Updated 13



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
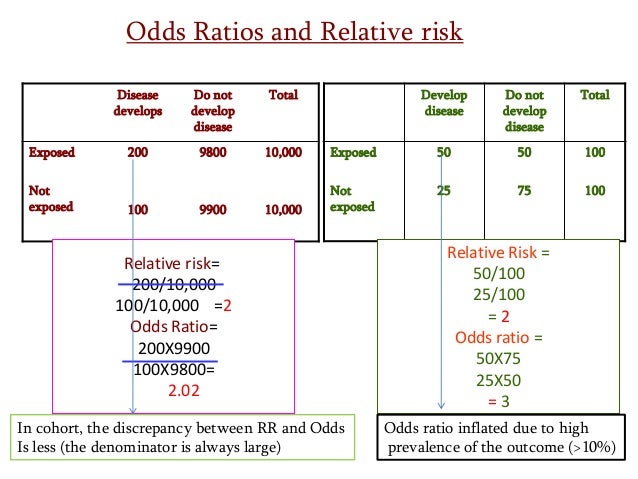


Estimating Risk



Odds Ratios From Univariate Regression Model Of Oasis Vs Risk Factors Download Table



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Risk Differences And Rate Differences


Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Relative Risk Ratio Interpretation



What Are The Odds Of Dying From Covid 19 Vs Lightning Wqad Com



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
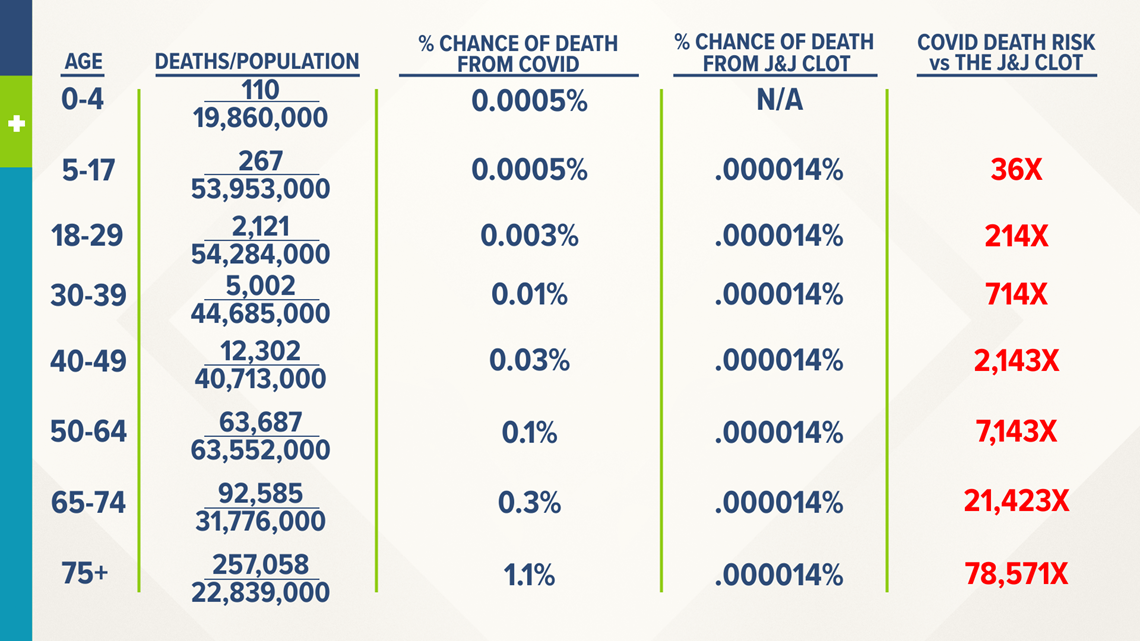


The Odds Of Dying From A J J Vaccine Related Blood Clot Vs Dying From Covid 19 Newscentermaine Com



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
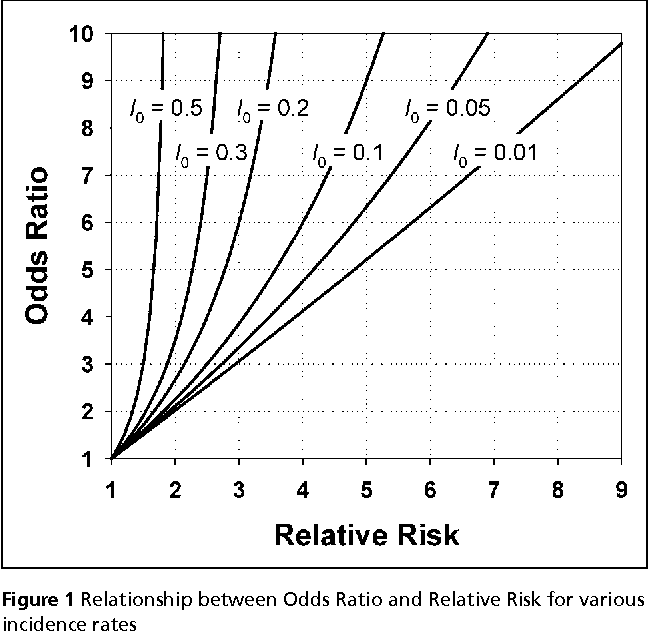


Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
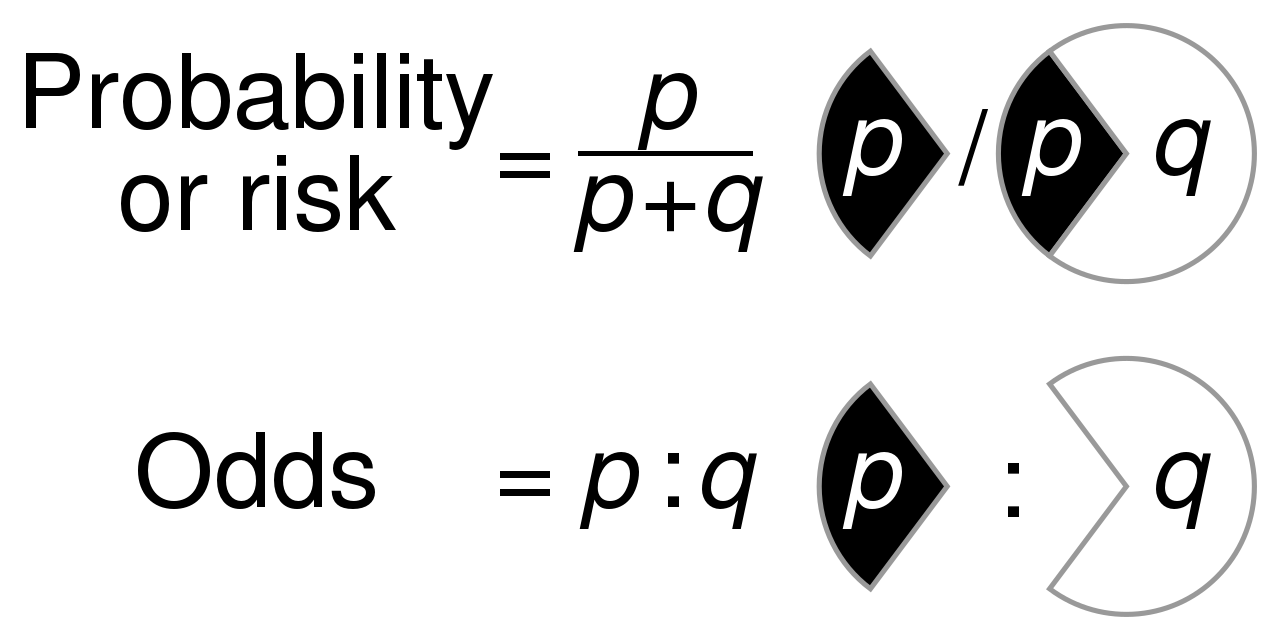


File Probability Vs Odds Svg Wikimedia Commons


Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream
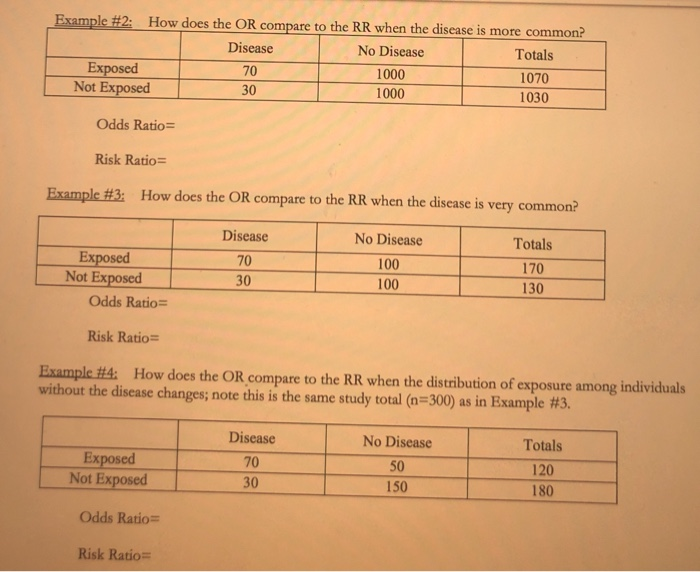


Solved Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿